How To Create A Winning Marketing Plan In 2023
Creating a marketing plan can be a tricky proposition. If you try to market your goods and services on how you want them to be viewed, rather than basing it on what the marketplace wants to see, you probably won’t get the expected returns. To create a marketing plan that ensures you receive the most benefit from your product development, sales, advertising, promotions, and public relations, seek to fill rather than create a need in the marketplace. Through this article, we provide an integrated framework that will transform the way you build marketing plans. The framework offers an integrated plan starting from strategy through execution process where each successive step builds on the preceding one to help develop a marketing plan grounded in sound business strategy.
How to develop Business Objectives?
Build on your core competencies
To plan your business goals, you must begin by reflecting on your core competencies. What is it that you are good at? What is that one thing/s that sets you apart from your competition? A realistic understanding of your core competencies will help you build a sustainable competitive advantage.
Below are a few characteristics of sound business goals:
- Measurable – Goals of an organization must be measurable. Quantified objectives give the business a clearly defined target. Without them, progress cannot be measured
- Achievable – Be realistic about your goals. While your vision may be to reach for the stars, your objective should be to first build your spaceship.
- Flexible – A business is tried and tested with the unpredictable waves of the market. Your business goals should be flexible and adjustable so that you can adjust to the wind and not capsize.
- Specific – Vague objectives will lead to vaguer results. Be specific about your objectives in terms of time, quality, and quantity.
- Hierarchical – Prioritize your objectives by importance and urgency. As we said earlier, the first aim to build a spaceship, then to purchase fuel, and then aim for the stars.
Once you figure out these business objectives, you can now convert them into marketing objectives, to develop a robust marketing plan.
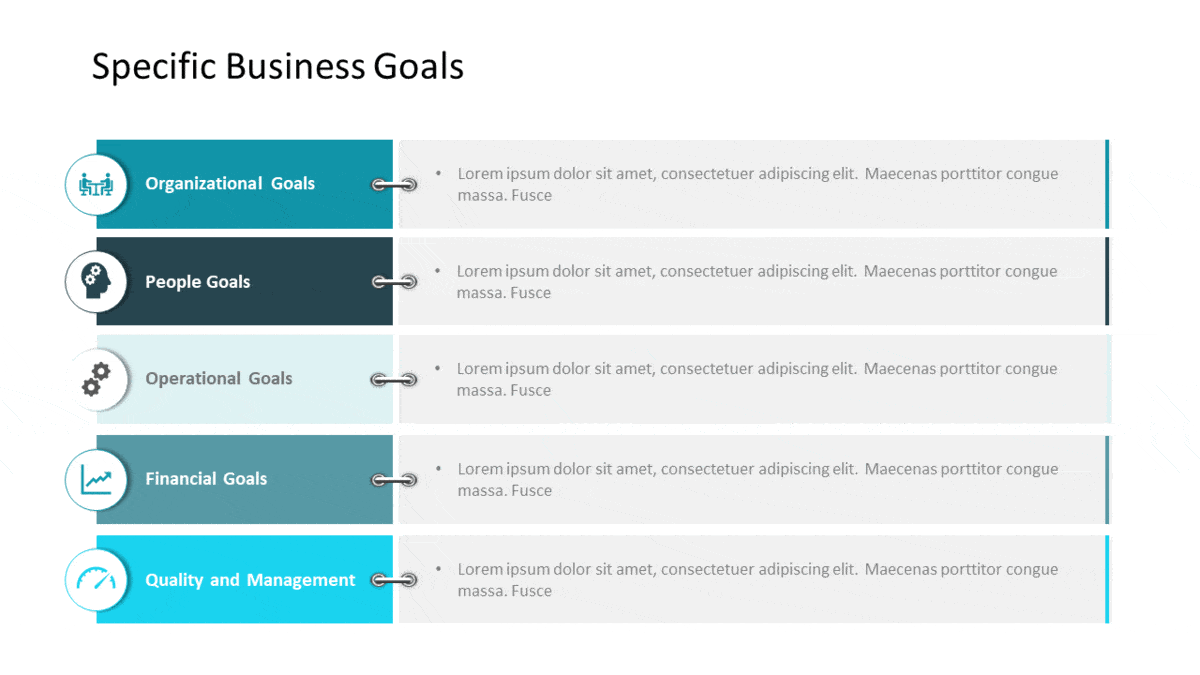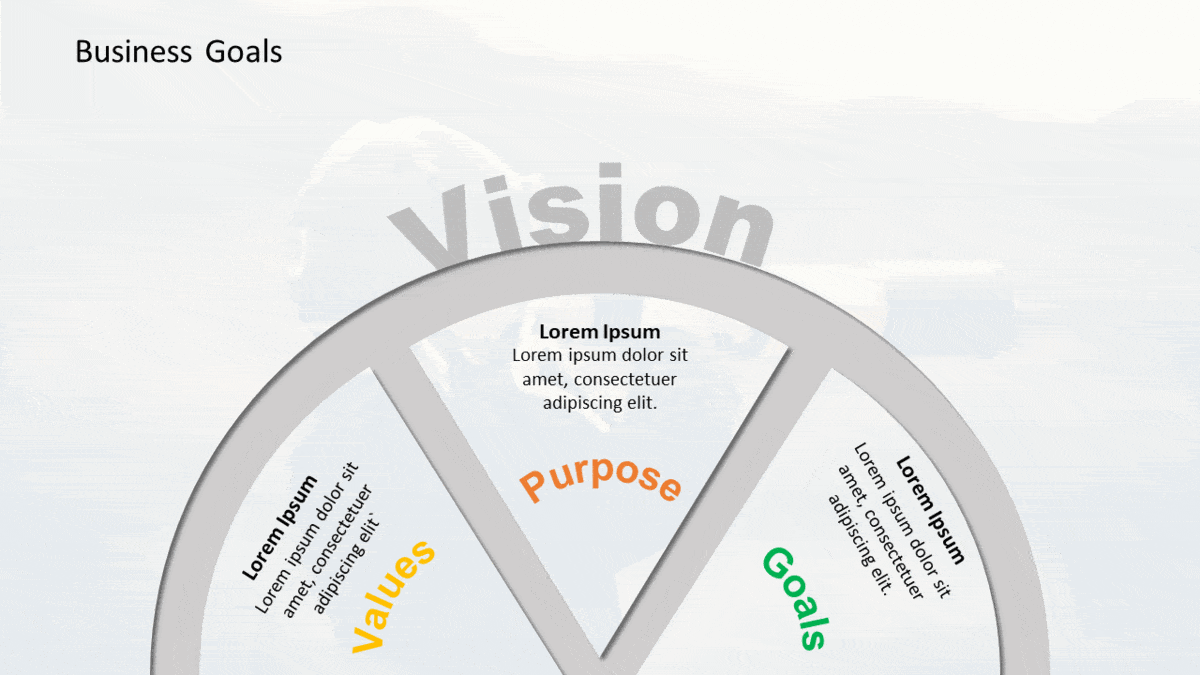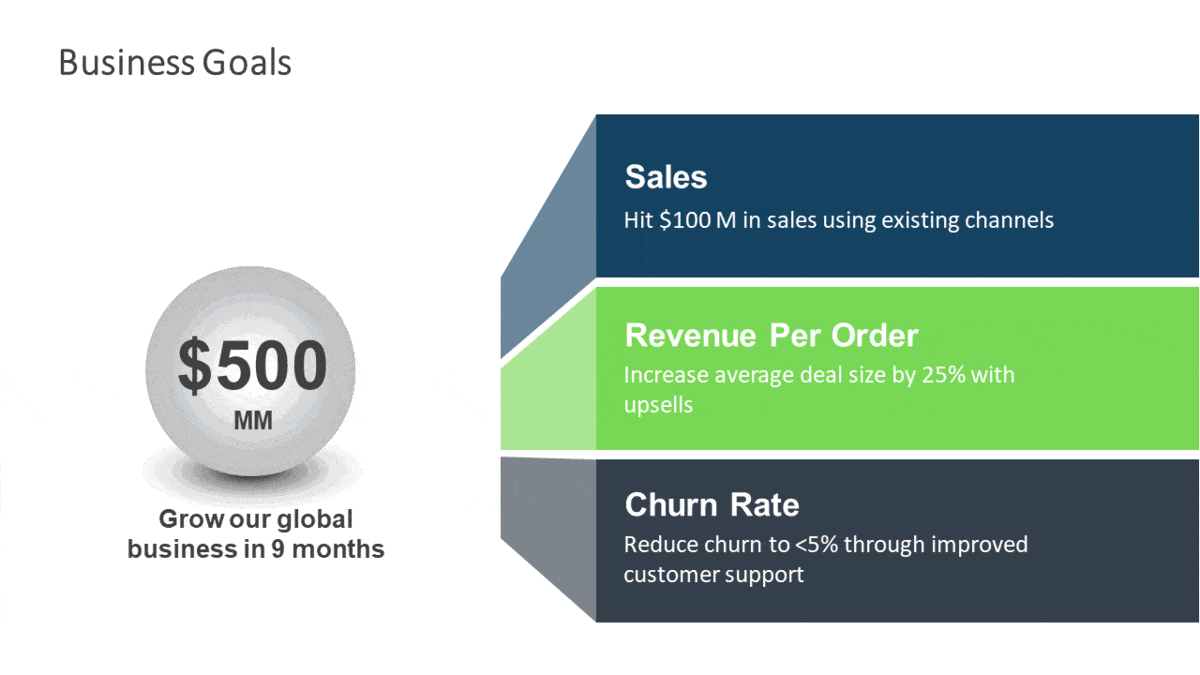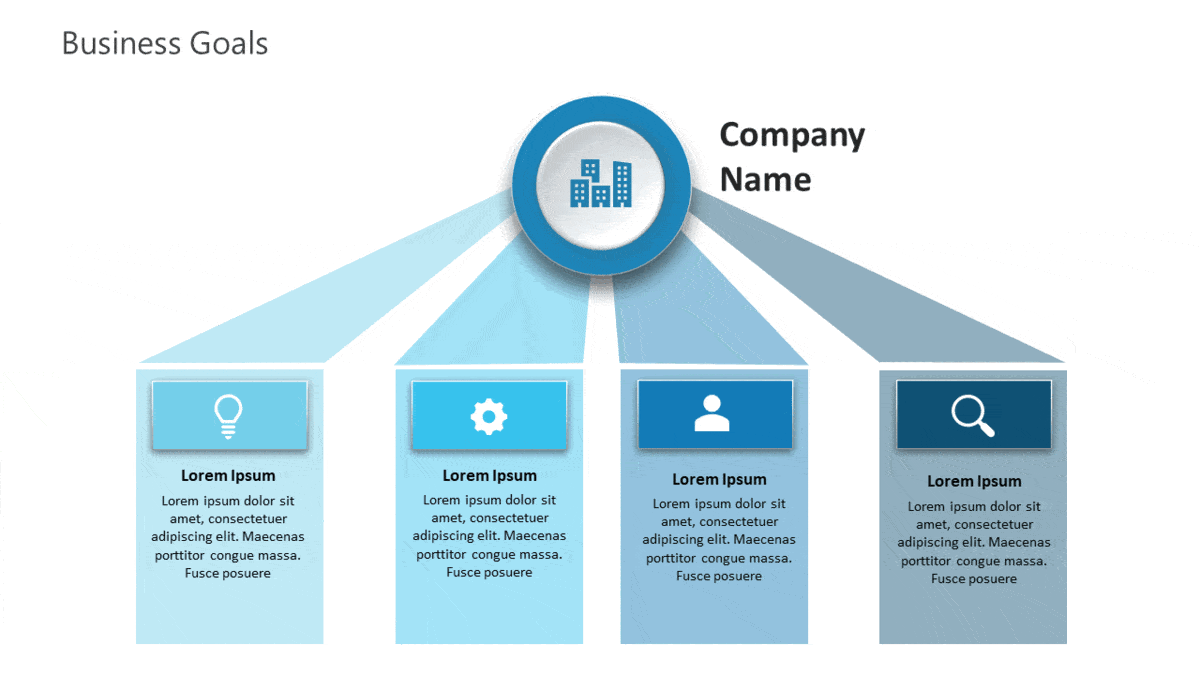
Example of a good Business Goal:
Business Objective: Grow our global business by $500MM
- Key Result: Hit $100 M in sales
- Key Result: Increase average deal size by 25% with upsells
- Key Result: Reduce churn to <5% through improved customer support
A few examples of Business Goals Templates:
How to develop Marketing Objectives?
A marketer’s goal is to eventually increase revenue. In the business world, there are two major levers of increasing volume and revenue.
Customer Acquisition
Wherein Marketing goals primarily focus on increasing the customer base by acquiring new customers.
Growth can come from stimulating demand, growing your category through product or business process innovation, or stealing shares, from competitors or substitute products in adjacent categories.
Customer Retention
Wherein Marketing goals focus on retaining existing customers of the product and increasing their consumption of the brand.
Depending on your product, category dynamics, and customer base, you have to allocate resources to customer retention vs customer acquisition.
The factors which help you decide whether you choose to acquire customers or retain them depending on your business status and objectives at that point in time. A few pointers are:
- Retention is usually cheaper and it is a low-hanging fruit
- If the business objective is growth, then customer acquisition is important
- Acquisition gets expensive without a solid retention
Now that we know our objectives, it is important to understand your customer well to develop a marketing plan around what he values.
Example of a good Marketing Goal
To increase Ecommerce revenue by 10%
- Website Traffic: Increase by 5% traffic each month
- Engagement Rates: Increase Engagement Rates on the website by 10%
- Follower Count: Increase Follower Count on Facebook by 5% each month
- Conversions: Increase the conversion of your visitors by 5%
How to develop Marketing Plan?
Know Thy Customer
The Customer – The customer is who you are trying to convince. So you should be aware of their needs, their aspirations, their problems, and their situations. Can you hit a target when blindfolded? The answer is an obvious NO. Similarly, you cannot think of a perfect market strategy without the knowledge of your target customers. That’s where customer segmentation comes into play.
Customer segmentation helps to have a better understanding of the target customers. It is essentially a division of potential customers into discrete groups. You can divide potential customers based on,
- Demographics like age, income group, cultural preferences, and occupation.
- Their needs like Physiological Needs, Safety Needs, Love and Belonging, Esteem and Self Actualization
- Their buying characteristics. For example – their responses to discounts, different messaging and marketing channels, etc.
Segmenting customers will help you select the segment for whom your offerings will be most relevant and will be aligned with your business and marketing goals.
Targeting
Now within the defined customer segment, we need a way to figure out how to target them the right way. To understand what drives your consumers, you need to first understand the consumers themselves.
Create a consumer profile for your chosen customer segment. Such a profile will describe your customer in detail – in terms of age, gender, income level, needs, aspirations, problems, behavior, attitudes, etc. This profile will give you a detailed picture of what your average customer in the segment looks, thinks, and acts like.
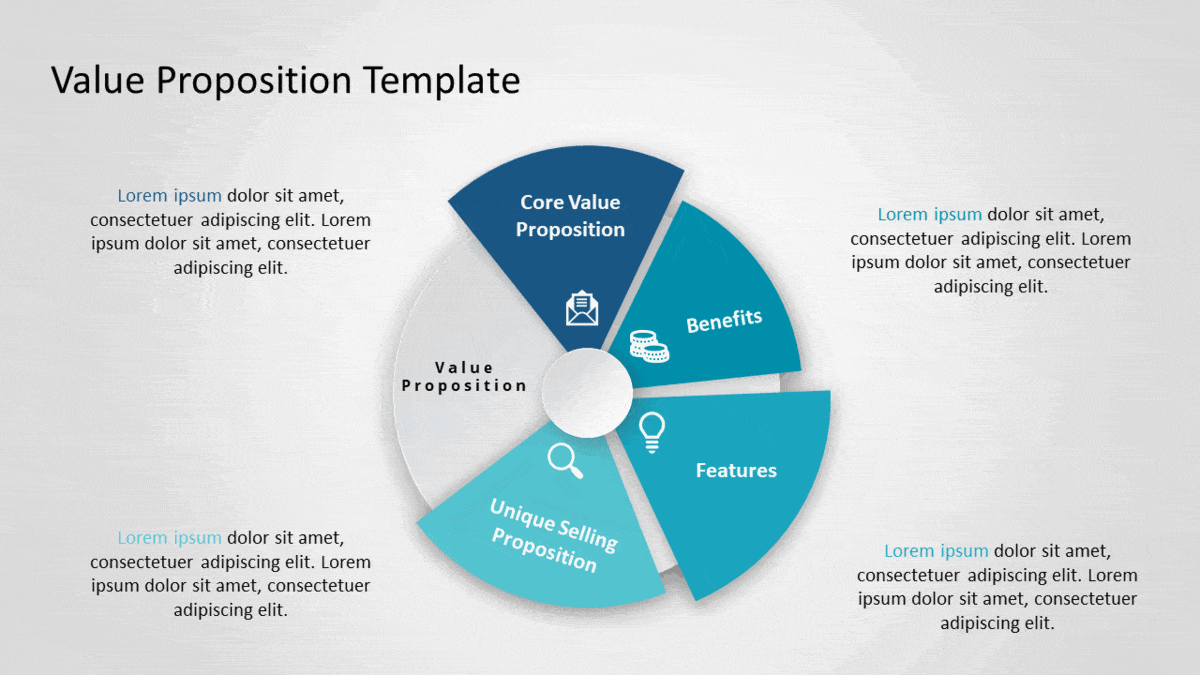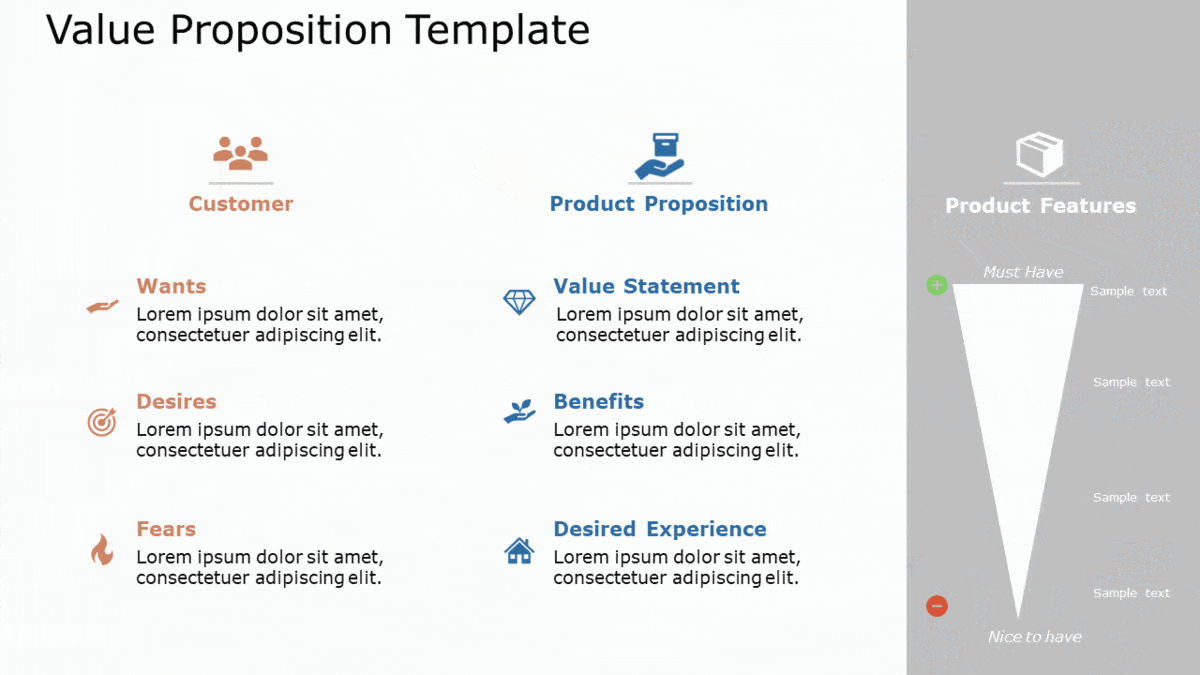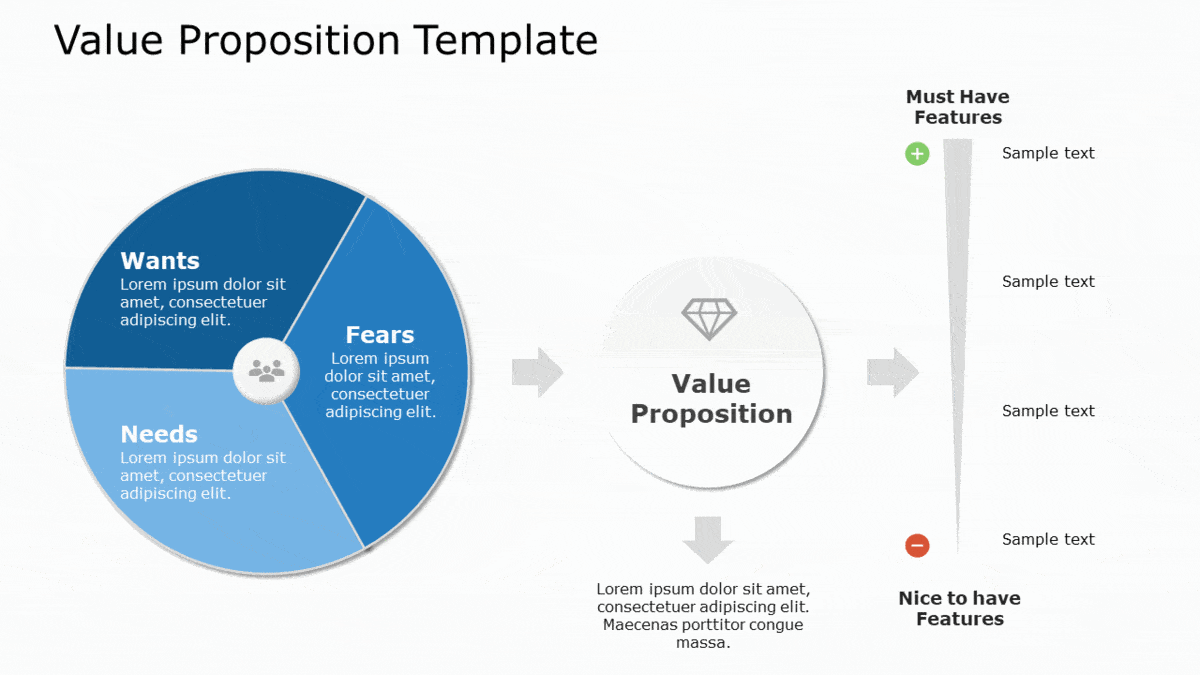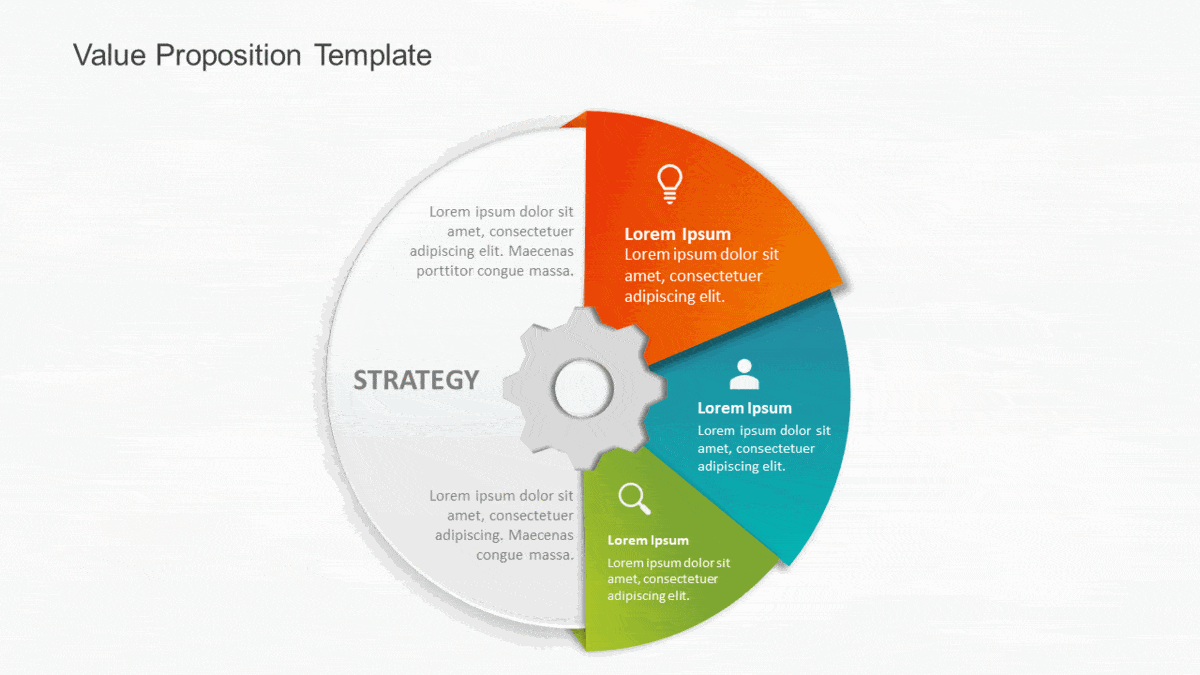
Value Proposition
The next step should be to describe what sets your product or service apart from competitors for your target audience. It gives a big-picture overview of the benefits a product or service provides for your target audience and how you are differentiated in the market.
A good Value Proposition is a clear statement that offers three things:
- Relevancy. Explain how your product solves customers’ problems or improves their situation.
- Quantified value. Deliver specific benefits.
- Differentiation. Tell the ideal customer why they should buy from you and not from the competition.
A few examples of Value Proposition templates:
Positioning Statement
Positioning statements are more focused, and they’re created after you’ve developed your business’ value proposition. It identifies only the primary customer benefits and points of competitive differentiation.
At its core, it’s a statement of how you want your brand to be perceived. It’s meant to be used as an internal tool to align marketing efforts with the brand and value proposition.
Effective Guidelines for writing positioning statements:
- Keep it brief.
- Make it unique and memorable.
- Remain true to your business’s core values.
- Include a credible promise of what the brand delivers to consumers.
- Communicate how your business is different from the competition.
- Keep it clean enough for use as a guideline to evaluate whether or not business decisions align with the brand.
Example of Positioning Statement:
Amazon Positioning Statement:
Target Audience: For consumers who want to purchase a wide range of products online with quick delivery,
Value Proposition: Amazon provides a one-stop online shopping site.
Reason to Believe: Amazon sets itself apart from other online retailers with its customer obsession, passion for innovation, and commitment to operational excellence.
Executing the Plan
4 P’s is the bedrock of any marketing plan. Once the needs and desires of the customer are verified, the 4Ps together help the firm in executing the marketing plan. Now let us discuss the four fundamental elements of the marketing execution plan which are the Product, Pricing, Promotion, and Place.
Product
The product concept is a combination of planning, producing, and developing the product or service to satisfy the ultimate need or want of the customer. It includes both tangible and intangible elements:
- Product range
- Warranty against defects
- Size and design of the product
- Branding
- Quality
- Packaging and Labelling
- After-sale services
Price
The primary criterion for deciding on the price is based on the purchasing power of the customers. The price of the product is determined by:
- Firm’s Objective
- Cost of Production
- The demand of the customer
- Competition
Place
The place is all about how the product reaches the manufacturer to the customer. The margin of your profit depends on how quickly you can turn over the goods. The more swiftly the products reach the point of sale, the more likely the chances of satisfying the customers and increasing brand loyalty. Hence the Place factor is crucial in ensuring your product’s competitiveness in the market. The following are the elements of a distribution mix:
- Channels of distribution
- Warehousing decision
- Product handling
- Transport
- Inventory control
- Order processing
- Coverage
Promotion
Now is the time to push your product. A key skill for a marketer is to know what information should be promoted through which mediums, and in what manner. The right promotion and mediums will directly resonate with your target customers. The main elements of a promotion mix are:
- Advertising
- Personal selling
- Public relations
- Direct marketing
- Publicity -social media, print, etc.
- Sales promotion
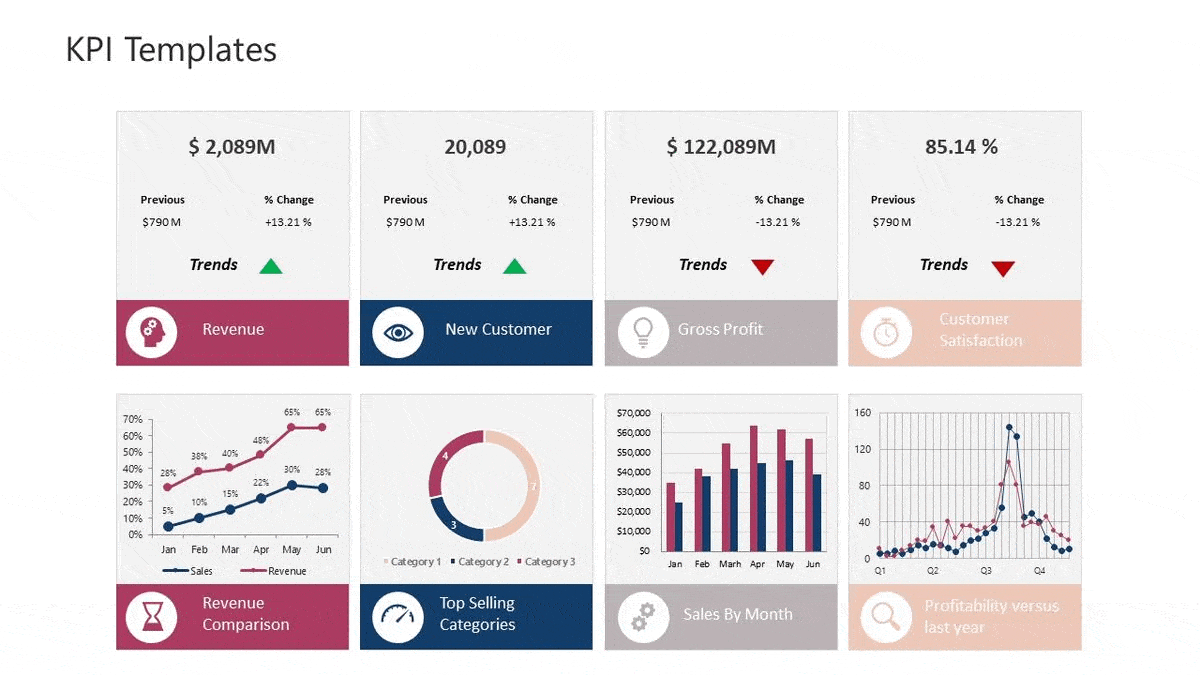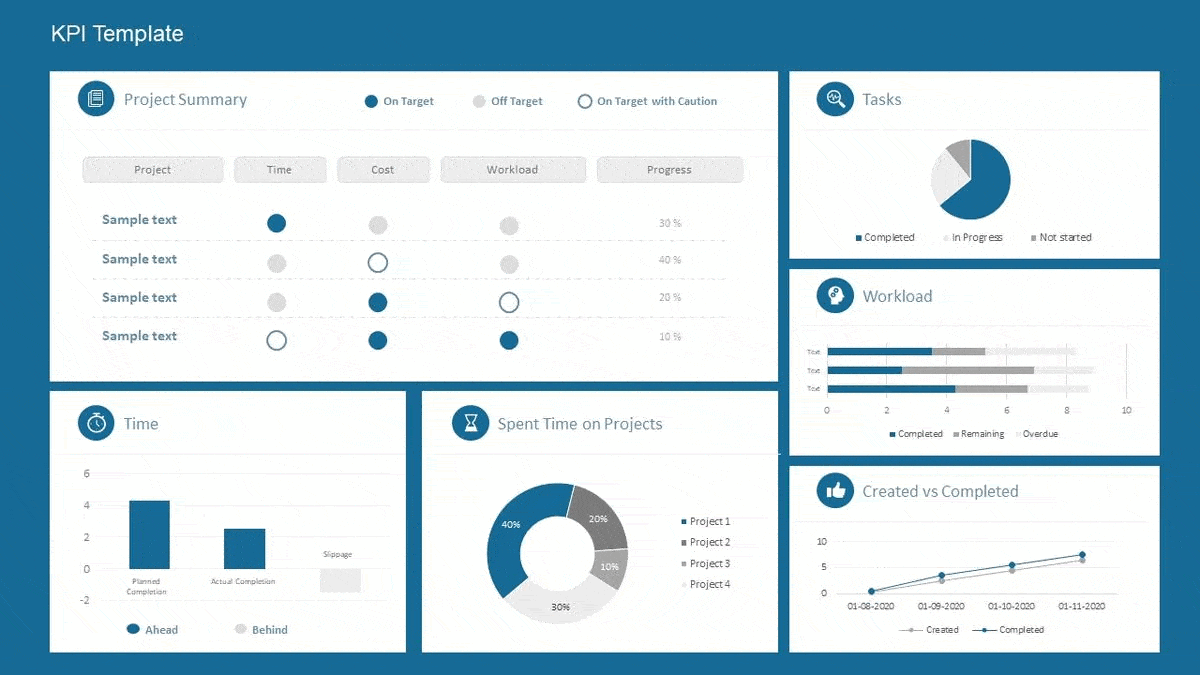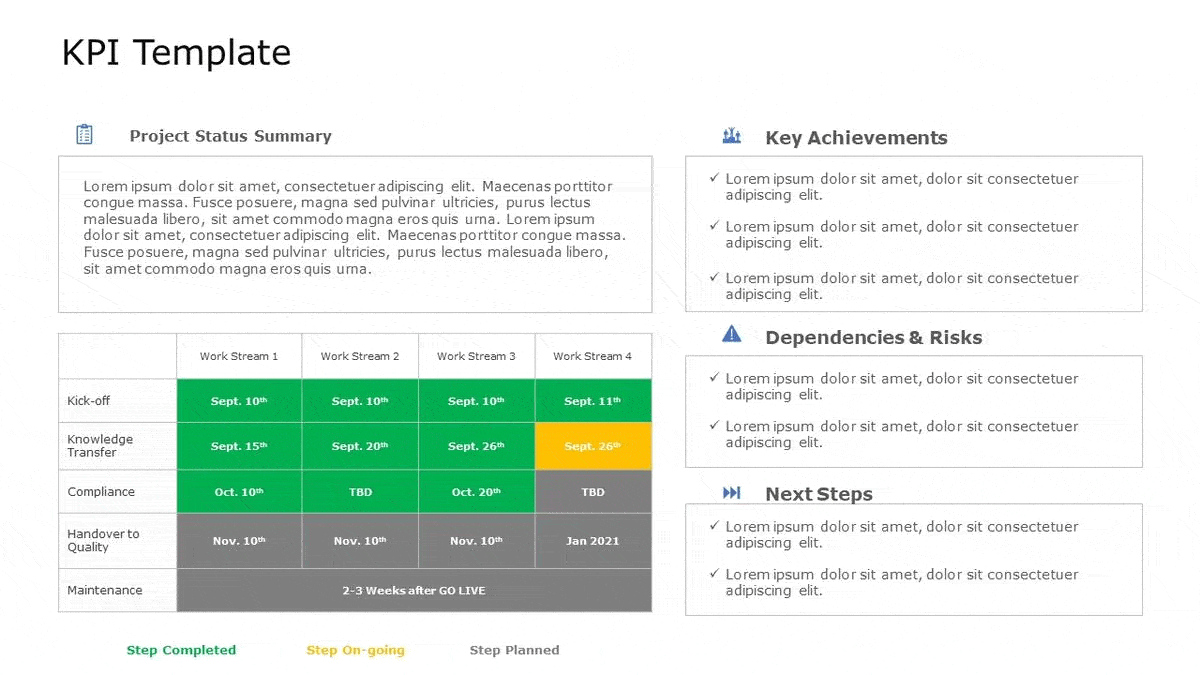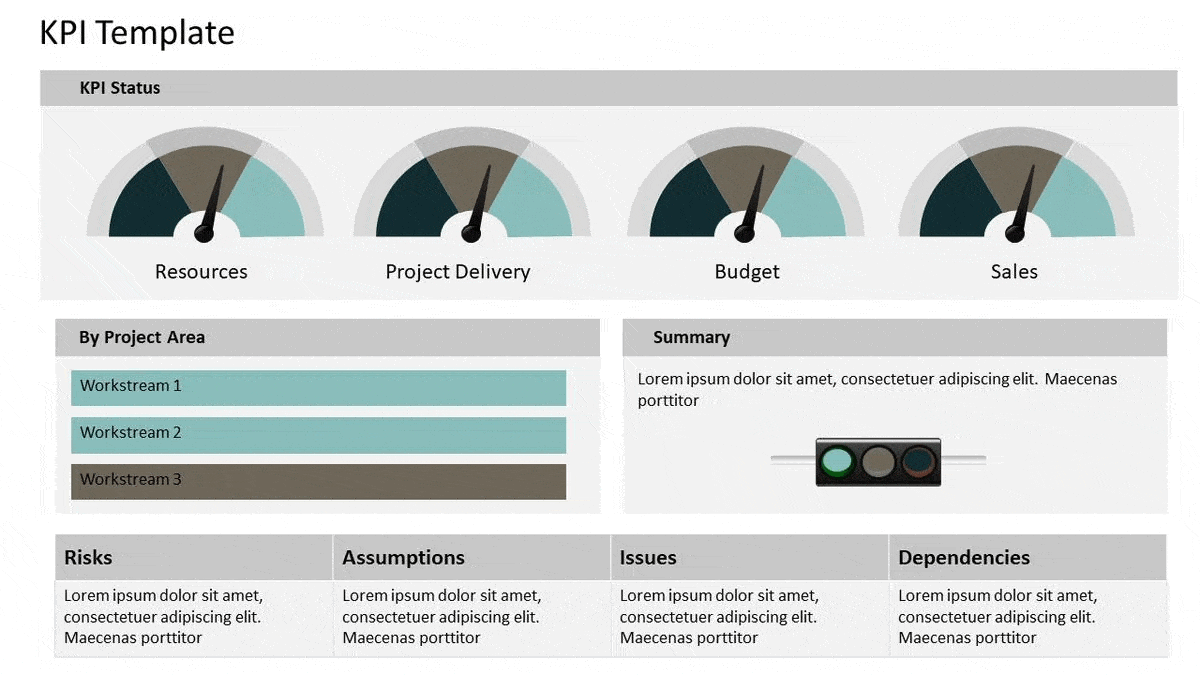
Tracking and KPIs
KPIs are important to business objectives because they keep objectives at the forefront of decision-making. All our marketing initiatives should be evaluated on the KPIs we define for our marketing plan.
Marketing KPIs are specific, numerical marketing metrics that organizations track in order to measure their progress toward a defined goal within their marketing channels.
A few important KPIs to track are:
- Sales Revenue
- Cost Per Lead
- Customer Lifetime Value
- Inbound Marketing ROI
- Traffic-to-Lead Ratio (New Contact Rate)
- Lead-to-Customer Ratio
A simple marketing plan with a robust and grounded action plan can ensure your success in business. An example of a Marketing Strategy and Planning Deck.